Four water recycling trends and what to expect in 2025


As we approach 2025, it is an opportune time to reflect on the significant trends that shaped the water sector throughout 2024. From the ripple effects of evolving global regulations to a growing emphasis on conserving and reusing our most vital resource, the past year has underscored the importance of innovation, knowledge, and collaboration in addressing global water challenges.
Here are the top trends we’ve observed, offering valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities shaping the future of the water reuse industry.
Trend #1: Increased regulations and government involvement
State and local governments are taking a more proactive approach to water conservation to combat water scarcity, climate change, and environmental concerns. As discussed at a recent Water Security and Climate Resilience Roundtable at the White House which Epic participated in, regulatory frameworks like California’s Title 22 or Austin’s GoPurple initiatives are setting the stage for broader adoption of water reuse solutions. California recently approved direct potable reuse allowing recycled water to be used for drinking water. In Virginia, treated rainwater can now be used within the building and property boundaries for non-potable purposes. Compliance with regulations is pushing innovation in water treatment and monitoring technologies to ensure both safety and efficiency while making an impact reusing our resources.
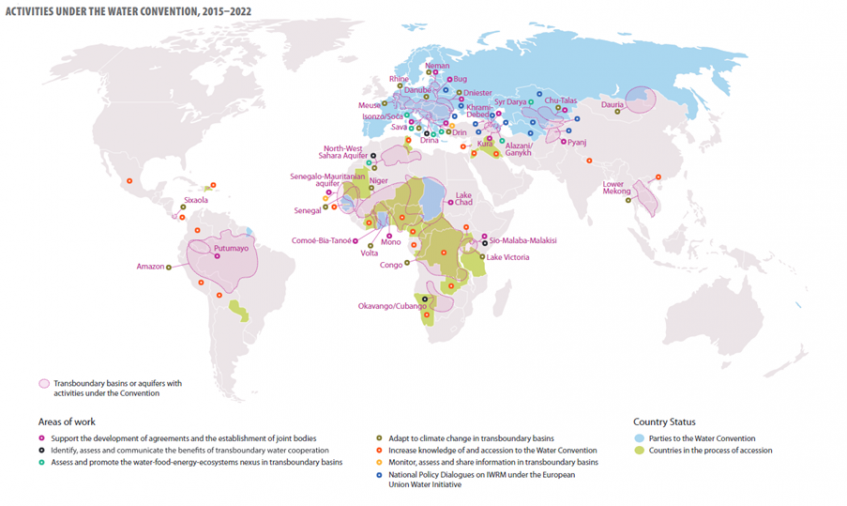
Cross-border collaborations are emerging as countries align policies to tackle shared water challenges. According to the United Nations, there are “153 countries that share rivers, lakes, and groundwater reserves that make up more than 60% of the world’s freshwater flow.” Collaboration on shared water resources serves as a crucial means to foster sustainable development, adapt to climate change, and advance peace and stability.
We’re also seeing an increase in grants, incentives, and subsidies become more common as part of government-backed sustainability initiatives. Recently, the National Science Foundation awarded the Southwest Sustainability Innovation Engine (SWSIE), an organization Epic is proud to partner with, $15 million over the next two years to help fund the initial development and growth of sustainable solutions in the Southwest. The increased visibility and funding of water is a trend we expect to see continue.
Trend #2: Rise of drought worldwide
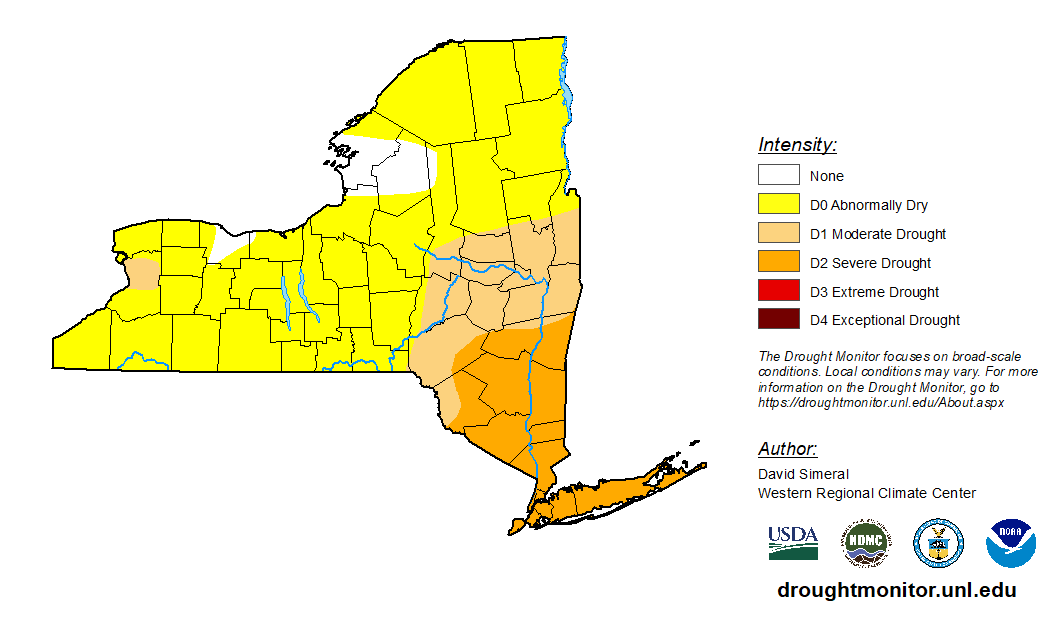
Droughts are no longer limited to arid regions—unexpected areas, including parts of Europe and the eastern U.S., are facing water shortages. In New York City, for example, a lack of precipitation in the fall caused a drought warning to be issued for the first time in 20 years as reservoir levels dropped below 60%.
Last year, 48% of our planet experienced at least one month of extreme drought, a significant increase from the 1980s average of 15%. A drought in southern Africa triggered by this year’s El Niño has caused a hunger crisis affecting over 27 million people, while Brazil, Chile, and Argentina all experienced significant drought in South America. Agricultural sectors are hit particularly hard as the industry is the largest consumers of water, driving up the cost of food while seeing less production.
However, the conversation is shifting from reactive to proactive solutions, prioritizing water reuse as part of long-term drought mitigation strategies. Solutions such as atmospheric water generation and desalination advancements are gaining traction in water-scarce regions. Municipalities are increasingly turning to water recycling as a critical component of drought resilience plans. Public awareness of water scarcity has heightened, creating more societal acceptance for recycled water usage and personal conservation techniques. And communities are recognizing the importance of decentralized solutions, such as onsite water reuse systems, to bolster resilience.
Trend #3: Addressing the water demand of AI and IoT
The rapid rise of artificial intelligence (AI), particularly generative models like ChatGPT and Gemini, has spotlighted the significant water usage tied to data centers, sparking widespread discussion over the past year. ChatGPT, for instance, uses an estimated quarter of a gallon of water for every 40–100 queries. Data centers, which support AI operations, consume vast amounts of water for cooling servers, are projected to have a 5.6% annual growth rate over the next decade. This increasing demand has raised environmental concerns, with major tech companies like Microsoft, Google, and Meta facing scrutiny over rising water consumption.
In response, we have seen an influx of leading tech firms committing to becoming “water positive” by 2030, implementing strategies such as water reuse, leak detection, and investments in water replenishment projects. Examples include Amazon Web Services (AWS) using reclaimed water for cooling and Microsoft funding leak detection projects. As AI accelerates the growth of the data center sector, significant investment in water-efficient technologies and infrastructure will be crucial to mitigating environmental impacts.
Trend #4: Upcycling wastewater into new resources
Globally, we’re seeing companies rethinking wastewater as a valuable resource rather than waste, and extracting nutrients, energy, biogas, and solids from it. They are seeking out partnerships to transform wastewater byproducts into usable goods, like Epic’s ability to recover organic solids and turn them into soil amendments. Upcycling creates a compelling sustainability narrative, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers, residents, and investors alike.
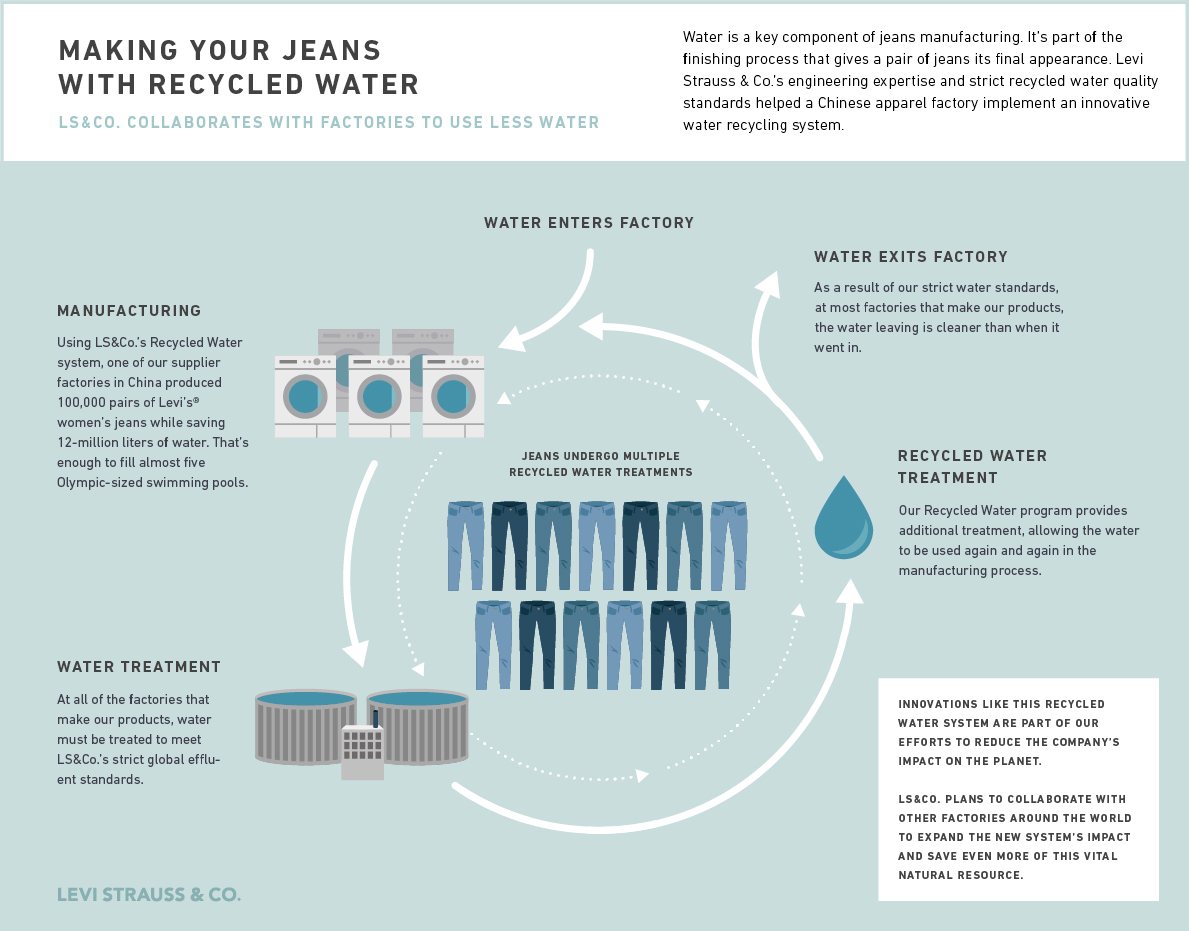
Upcycling wastewater is becoming a central focus for global fashion brands committed to sustainability. Levi Strauss & Co. leads with initiatives like Water<Less®, aiming to reduce freshwater use by 50% in high-stress regions by 2025. H&M integrates water stewardship into its operations, targeting a 30% reduction in freshwater extraction by 2030. Nike and Gap also recycle water for textile dyeing and support clean water access. Approaches like these demonstrate how wastewater can be repurposed into the creation of everyday products, even textiles.
Wineries, particularly in California, stand out when it comes to reimagining water use. Jackson Family Wines captures rainwater in winter to clean and cool wine cellars, diverting floodwaters into vineyards to replenish aquifers and improve water quality. Similarly, Cakebread Cellars uses permeable pavers and bio-swales in a green parking lot to capture and filter rainwater, while recycled water irrigates their gardens and landscaping.
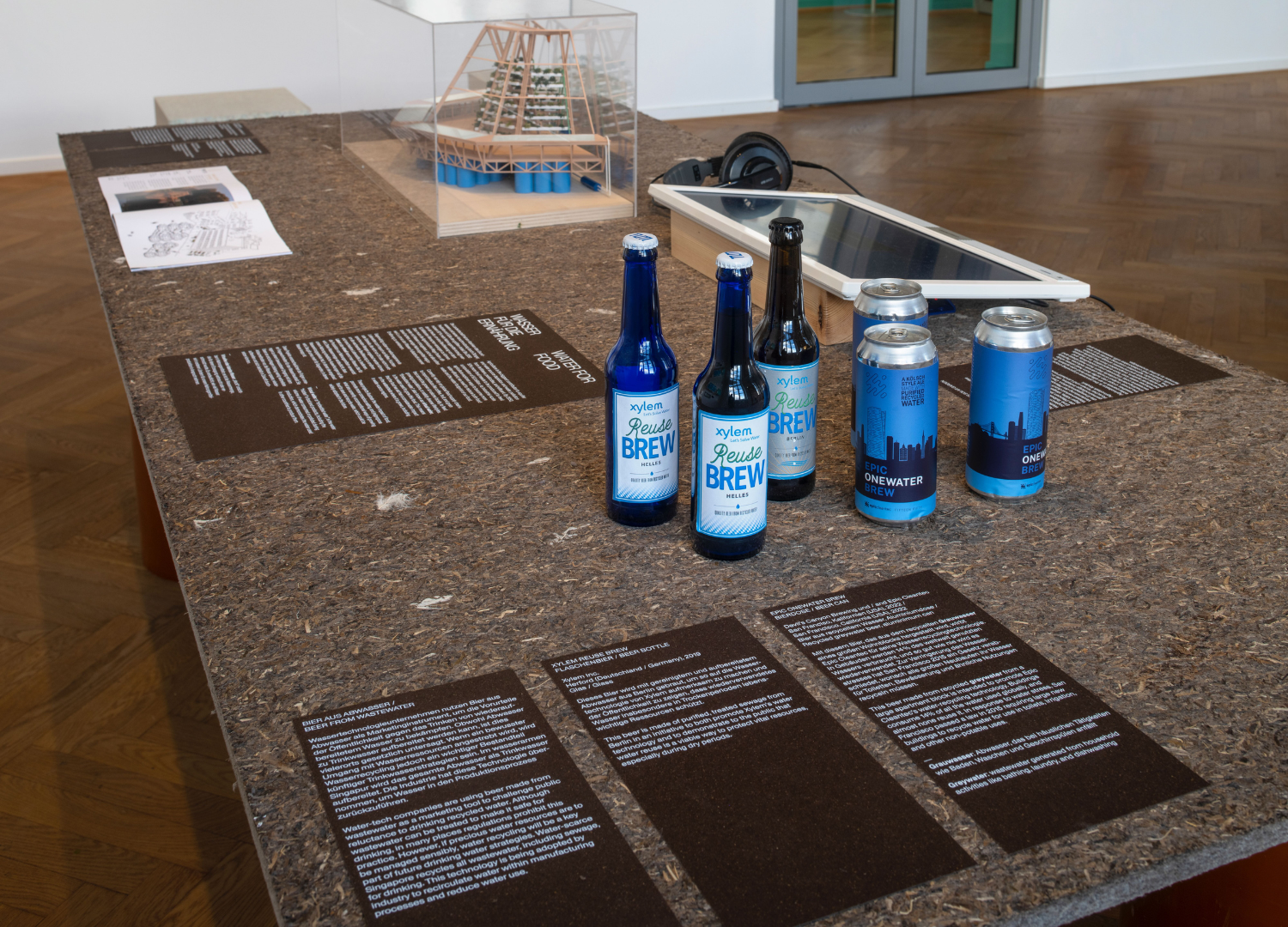
Breweries are also embracing sustainable sips by crafting beers with recycled water—an area in which Epic Cleantec has explored. Our partnership with Devil’s Canyon Brewing Company resulted in Epic OneWater Brew, a Kölsch-style ale made from recycled building greywater. Similarly, Singapore’s NEWBrew transforms treated wastewater into a modern pilsner, while Xylem’s Reuse Brew highlights cutting-edge water recycling technology with its Bavarian-style beer.

Predictions for 2025 and beyond
As we look ahead to 2025, climate-driven drought, aging infrastructure, and growing urban populations are reshaping water management.
The need for smart, connected platforms and infrastructure will be essential in building resilience. We predict seeing more partnerships among PropTech and solution providers to advance real-time reporting, water use insights and enhance decision making. This includes greater deployment of IoT sensors and AI-driven analytics for real-time water quality monitoring, leak detection, and predictive maintenance.
We also predict the need for wider adoption in technologies that integrate energy recovery within water systems (e.g., wastewater heat recovery or water-powered microgrids) as cities aim for energy-efficient and decarbonization solutions.
As water reuse becomes more essential, we need to preserve our freshwater supplies, enhance building resilience, and ease the strain on centralized systems with decentralized solutions. Cities like San Francisco, Austin, and Seattle are leading the charge, setting a precedent for sustainable water solutions.
At Epic Cleantec, we’re optimistic about the future as more business leaders, developers, and policymakers embrace water recycling and the growing recognition of water’s critical role in sustainability, public health, and economic development.